Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Regular Geometry
The underlying geometry (a.k.a. grid) is the foundation of a block model. Since parq-blockmodel is designed to work with regular geometries, this example demonstrates the underlying regular geometry by visualising it with PyVista.
import tempfile
import pandas as pd
from pathlib import Path
from seaborn import axes_style
from parq_blockmodel import ParquetBlockModel, RegularGeometry
Create Geometry
We RegularGeometry object (not a ParquetBlockModel). The geometry knows nothing about attributes, it only knows about the underlying geometry of the block model.
corner: tuple[float, float, float] = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
block_size: tuple[float, float, float] = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
shape: tuple[int, int, int] = (2, 2, 2)
geom: RegularGeometry = RegularGeometry(shape=shape,
block_size=block_size,
corner=corner
)
geom
RegularGeometry: {'corner': (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), 'axis_angles': (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), 'block_size': (1.0, 1.0, 1.0), 'block_count': 8, 'shape': (2, 2, 2), 'is_regular': True, 'extents': ((0.0, 2.0), (0.0, 2.0), (0.0, 2.0)), 'bounding_box': ((0.0, 2.0), (0.0, 2.0))}
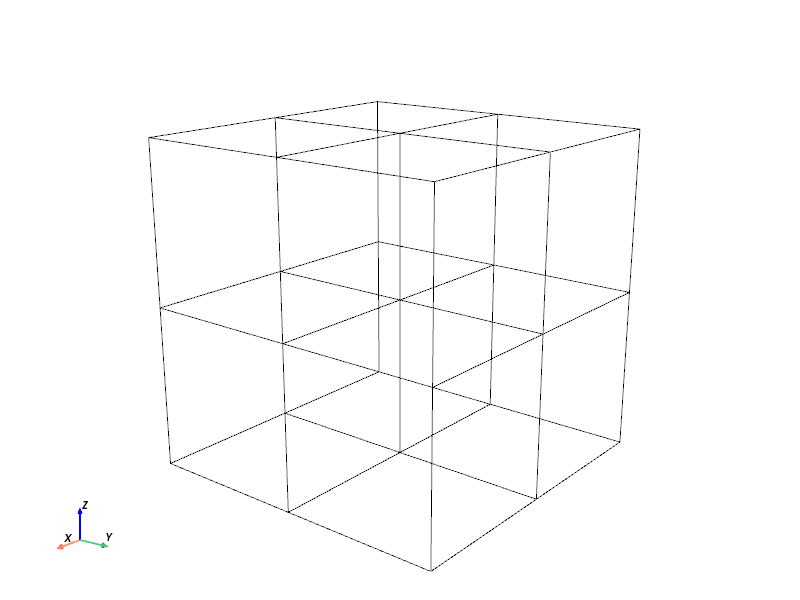
Visualise in 3D
Plot using PyVista. The geometry is a mesh, so we can use the plot method to visualise it.
import pyvista as pv
isometric_view = [
(6, 5, 3), # camera position
(1, 1, 1), # focal point (center of the grid)
(0, 0, 1), # view up direction
]
# Create a PyVista plotter
plotter = pv.Plotter()
edges = geom.to_pyvista().extract_all_edges()
plotter.add_mesh(edges, color="black", line_width=1)
plotter.show_axes()
plotter.camera_position = isometric_view
plotter.show(title="Regular Geometry", window_size=(800, 600))
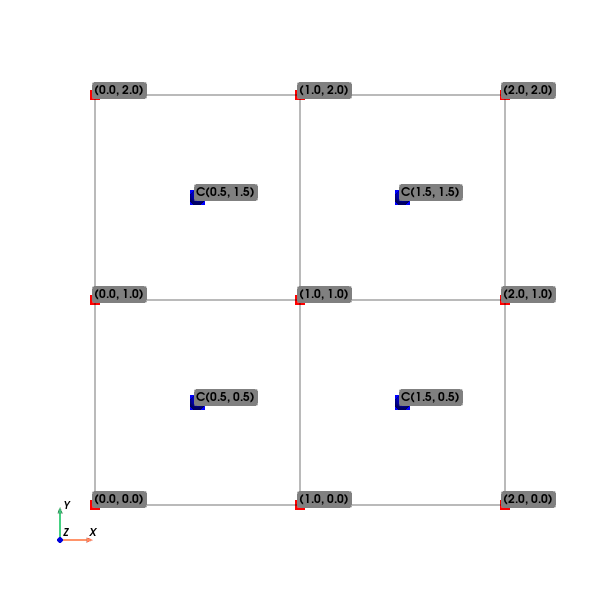
Visualise in 2D
In most cases a 2D visualisation is sufficient to understand the underlying geometry. We can use the to_pyvista method to get a PyVista mesh and then plot it in 2D.
grid = geom.to_pyvista()
# Slice at z=0.5 to intersect the first layer of cells
slice_2d = grid.slice(normal='z', origin=(0, 0, 0.5))
edges_2d = slice_2d.extract_all_edges()
points = edges_2d.points
labels = [f"({x:.1f}, {y:.1f})" for x, y, _ in points]
centroids_mesh = slice_2d.cell_centers()
centroids = centroids_mesh.points
labels_centroids_2d = [f"C({x:.1f}, {y:.1f})" for x, y, _ in centroids]
plotter = pv.Plotter()
plotter.add_mesh(edges_2d, color="black", show_edges=True)
plotter.add_point_labels(points, labels, font_size=12, point_color="red", point_size=10)
plotter.add_points(centroids, color="blue", point_size=15, render_points_as_spheres=True)
plotter.add_point_labels(centroids,
labels_centroids_2d,
font_size=12,
point_color="blue",
point_size=0, # Hide label points
always_visible=True,
render_points_as_spheres=False)
plotter.show_axes()
plotter.view_xy()
plotter.show(title="2D Slice with Corner and Centroid Coordinates", window_size=(600, 600))
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.291 seconds)